
Step to Create Data Strategy 3 – Business Intelligence
7. Develop a roadmap: Create a roadmap based on any recommendations. This roadmap could range from three to five years. For example, you were advised to start and increase the maturity of analytics. This is done in two major steps. The first step is to enable access to historical data, tools, and skills for individuals or groups of users, creating governance, policies, and procedures around the data. Once the quality of historical data is provided, advanced skills to create mathematical algorithms and statistics are achieved to advance to the next maturity levels. For example, historical data is required to find what happened, when, where, how, at what frequency. Next is to find the root cause of the problem. Finding out what action is required can also be done with the help of historical data and advanced analytics. Data science is one step ahead, using historical data to find what can happen next with reasonable confidence. Figure 7-13 is an example of a high-level roadmap.
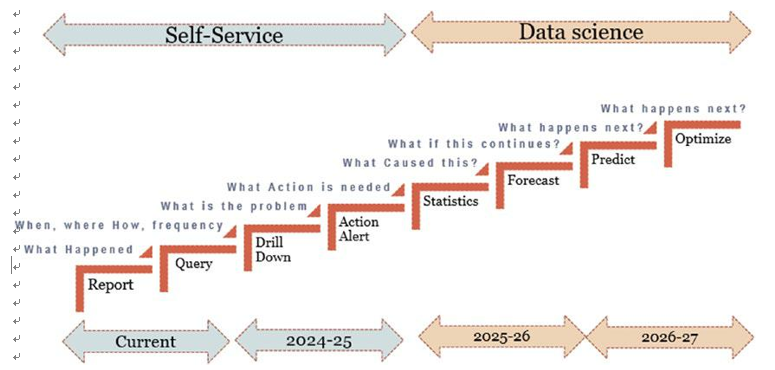
Figure 7-13. High-level roadmap
Figure 7-13 demonstrates a framework to increase the data science capabilities and maturity of an organization, from reporting to statistics to forecasting and predictive capabilities.
8. Develop a business use case: This step gathers requirements from a business for a specific use case. Gather costs and both qualitative and quantitative benefits to get from these use cases. Find dependencies of these use cases and fine-tune your roadmap based on the bandwidth and the budget allocated. Create specific projects associated with these individual or collection of use cases.
9. Prepare for change: This step prepares for a well-informed change management strategy. Create a plan that aligns with all stakeholders’ interests, and prioritize use cases. For the implementation of the data strategy, it is important to take all stakeholders on same page. Prepare council and committees and communication plans for all stakeholders and their involvement.
10. Execute the strategy: As the data management and business intelligence use cases increase with time, there is a requirement to improve speed in delivering trusted data. Focus on value where there is business impact. Increase the collaboration across data, business, and technical persons. Manage interdependencies across business process. Provide reliable data-delivery service goals and levels.
Operational excellence in data delivery is achieved through predictability in delivery and change management of data.
As tracking of metrics—such as time to deploy changes, degree of automation, developer productivity, code quality, and cost efficiencies in dollar amount—increases, failure rates in production decrease. Direct benefits of DataOps are increased productivity, reduced development timelines, and a robust pipeline to ensure
that pipelines don’t break frequently and are designed in such a way that change management and fixes can be done easily to ensure lineage, security, and quality.
Self-service analytics required advanced tools that require building descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive capabilities. However, data management with drag-and-drop capabilities are limited to descriptive capabilities.
Data science and machine learning platforms require governance of data science models and tools.
Archives
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- May 2023
- March 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- August 2022
- June 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- October 2021
- August 2021
- June 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- January 2021

Leave a Reply